ngSkinTools2 API¶
Introduction¶
Welcome! You’ve reached documentation for ngSkinTools2 API.
ngSkinTools2 is meant to be used primarily from UI. However, it is possible to access some of it’s functionality from Python.
Note
Usage examples in this documentation are automatically tested with latest plugin build, so if they don’t work with your ngSkinTools2 version, consider updating.
Architecture at a glance¶
ngSkinTools2 is built of the following layers:
C++ binary. Implemented as a standard Maya plugin, it provides plugin-specific commands and node types. This is where most of the computing heaving-lifting is done; the exposed functions and objects are not intended to be used directly, therefore the lack of documentation for plugin itself;
API layer in Python - everything in ngSkinTools2.api namespace. This section of the code is decoupled from Maya’s UI and provides a slightly higher level of abstraction on top of the C++ binary. This namespace is intended to be usable from outside of the plugin as well;
UI layer in Python - provides the end-user interface of ngSkinTools. This part is not intended to be reusable. However, as UI builds on top of the API layer, it might serve you as example of how the API is intended to be consumed.
This documentation primarily focuses on API layer.
IDE setup¶
If you have IDE that is able to parse documentation from code, consider configuring your project to index ngSkinTools2 source directly.
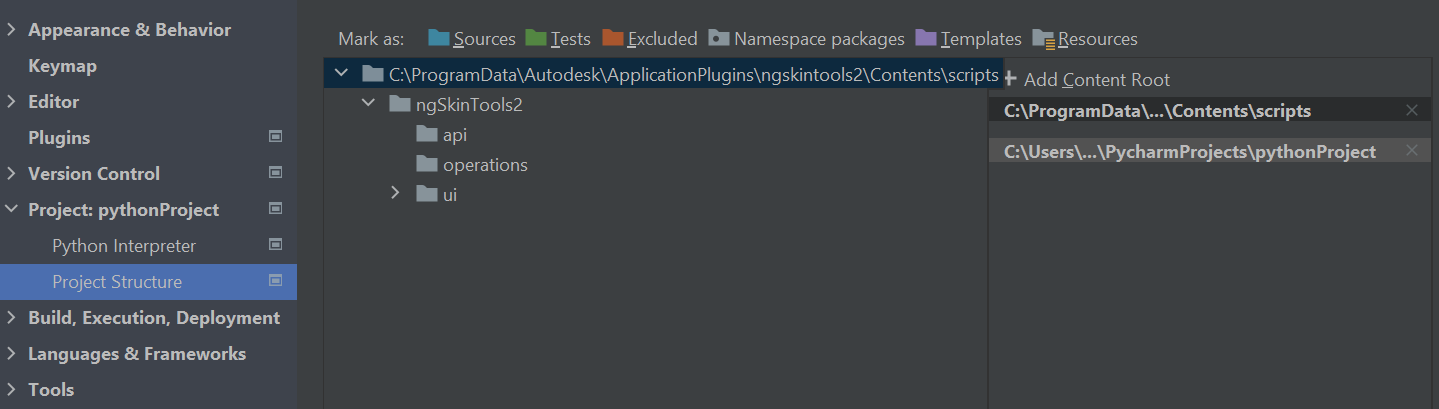
For example, in PyCharm, go to Settings | Project | Project Structure, click “Add Content Root” and select ngSkinTools2/Contents/scripts directory from where ngSkinTools2 is installed.
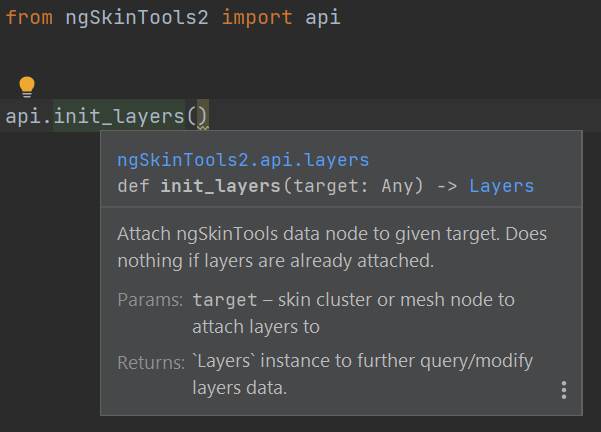
After configuring this, you should be able to see documentation directly in UI, and have auto-complete on various API objects, e.g. attributes for Layer properties. For example, press ctrl + q to quickly check function reference.